Introduction
Welcome to the website of Nagpur Zilla Parishad. Efforts have been made to make the website public oriented while making it functional for citizens of all walks of life. While adopting the government’s information and technology policy, G.P. The various schemes and its complete information as well as the information of various departments have been made available on the website. To the people of all levels of the state, G.P. Information about the work done in can be viewed through the website
Panchayat Raj is an innovative experiment in the making of modern India.
The Balwantrai Mehta Committee has recommended a three-tier Panchayat Raj system to involve the rural masses in rural development.
Accordingly, the Government of Maharashtra passed the Maharashtra Zilla Parishad and Panchayat Committees Act, 1961 on 1 May 1962 and established a three-tier Panchayat Raj at the district level, Zilla Parishad at the group level, Panchayat Samiti at the village level and Gram Panchayat at the village level.
self Nagpur Zilla Parishad was established in May 1962 under the guidance of Yanshawtraoji Chavan. Shri Chhatrapal Anandrao Kedar had the honor of being the first President of Nagpur Zilla Parishad. He d. Held the post of President of Zilla Parishad from 12.08.1962 to 11.08.1967. Since then, 22 presidents have held this post in Zilla Parishad Nagpur.
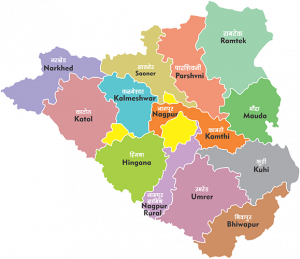
Zilla Parishad Nagpur has 13 panchayat committees and 770 gram panchayats working for rural development and there are 1872 villages in them. Zilla Parishad Nagpur has always been a leader in implementing any scheme, mission, campaign of the government.
The purpose of the Zilla Parishad is to implement the plans for the development of the rural areas by the Central Government and the Maharashtra State Government and to supervise those plans. Also, to deliver these schemes to the villagers through the Panchayat Samiti and Gram Panchayat and to achieve the development goals in the rural areas and to develop the rural areas comprehensively.
| Sr No. | Matter | Statistics |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total Panchayat Committees | 13 |
| 2 | Gram Panchayat | 759 |
| 3 | Inhabited villages | 1,827 |
| 4 | Total population | 46,53,570 |
| 5 | Rural population | 15,13,588 |
| 6 | Sub-caste population | 2,69,350 (16.10 percent) |
| 7 | Sub-Tribal Population | 2,10,293 (12.36 percent) |
| 8 | Total Family Number (APL) | 234696 |
| 9 | Total Family Number (BPL) | 91,873 |
| 10 | Overall rural literacy rate | 78.95 percent |
| 11 | Number of Gram Panchayat Members | 7,034 |
| 12 | Number of female members | 3,944 |
| 13 | Number of male members | 3,090 |
| 14 | Caste Member No | 1,183 |
| 15 | No. of Tribal Members | 975 |
| 16 | Geographical area | 9812 sq.km |
| 17 | Forest area | 2,538 sq.km |
| 18 | General area under crop | 6,33,212 hec. |
| 19 | Area under kharif crop | 4,74,324 hec |
| 20 | Area under Rabi / Summer crops | 1,81,109 hec |
| 21 | Aggregate Small Irrigation Ponds / Dams | 10 |
| 22 | Villages with tap water supply | 1512 |
| 23 | Average annual rainfall | 1147.50 |
| 24 | Primary school | 1502 |
| 25 | Secondary School | 14 |
| 26 | Number of Anganwadis in operation | 1951 |
| 27 | Rural Hospital | 10 |
| 28 | Primary Health Centre | 53 |
| 29 | Primary Health Sub-Centre | 316 |
A committee headed by Balwant Rai Mehta recommended a three-tier Panchayati Raj system in 1957. The Government of Maharashtra established the Maharashtra Zilla Parishads and Panchayat Samitis Act 1961 and adopted the three-tier Panchayat Raj system on 1 May 1962 under the Act.
District Map