Objectives & Functions
Objectives
The Zilla Parishad Nagpur is a local self-government body in the Nagpur district of Maharashtra, India. Its primary objective is to promote rural development and ensure effective governance at the grassroots level. Here are some key objectives of the Zilla Parishad Nagpur:
- Rural Development: Implementing various development programs aimed at improving the living standards of rural populations, including agriculture, irrigation, and infrastructure development.
- Education: Enhancing educational facilities and promoting literacy in rural areas by establishing schools and providing necessary resources.
- Health and Sanitation: Improving healthcare services and sanitation facilities in villages to ensure better health outcomes for the rural population.
- Women Empowerment: Promoting gender equality and empowering women through various schemes and initiatives.
- Employment Generation: Creating job opportunities and promoting skill development programs to reduce unemployment in rural areas.
- Sustainable Development: Focusing on sustainable practices in agriculture and resource management to ensure long-term ecological balance.
- Community Participation: Encouraging active participation of local communities in decision-making processes and development initiatives.
- Infrastructure Development: Developing rural infrastructure such as roads, transportation, and communication facilities to enhance connectivity and accessibility.
- Social Welfare: Implementing social welfare schemes for marginalized and disadvantaged groups to ensure inclusive development.
- Coordination with Government Schemes: Aligning local development initiatives with state and central government schemes to maximize resource utilization and effectiveness.
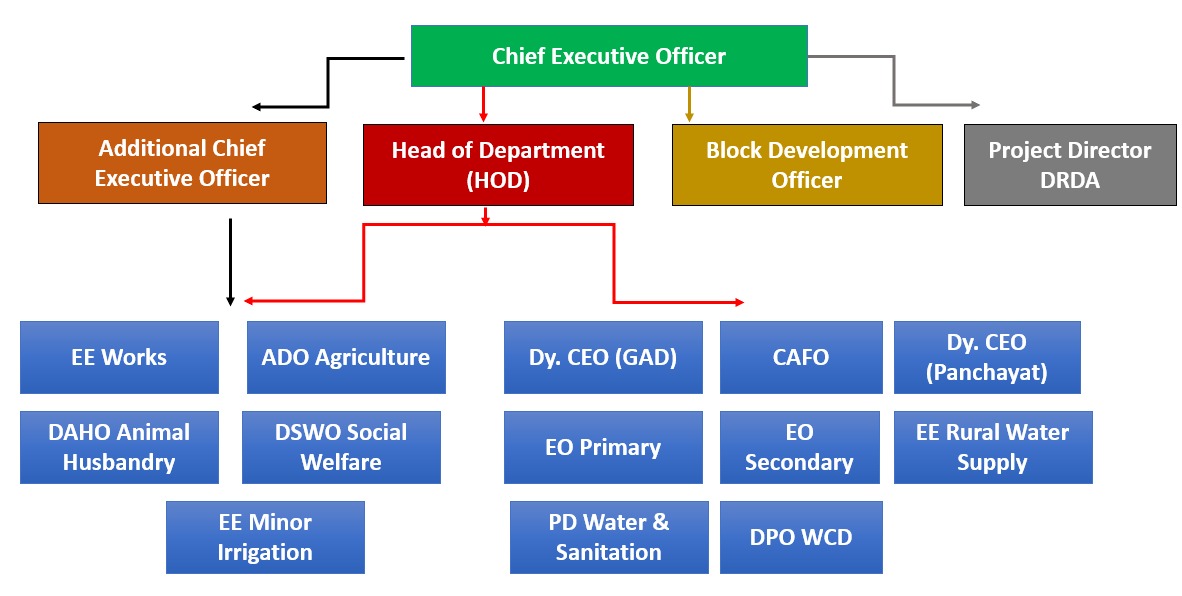
Functions
The Zilla Parishad (ZP) is a key institution in the Panchayati Raj system in India, responsible for the governance and development of rural areas at the district level. The functions of the Zilla Parishad can be broadly categorized into various areas:
- Planning and Implementation of Development Programs
- Formulating and implementing development plans for the district, focusing on agriculture, rural development, and infrastructure.
- Coordinating with various government departments to ensure the effective execution of development schemes.
- Education
- Establishing and managing schools and educational institutions in rural areas.
- Promoting adult education and literacy programs.
- Ensuring the quality of education and infrastructure in schools.
- Health and Sanitation
- Implementing health programs and initiatives to improve healthcare services in rural areas.
- Promoting sanitation and hygiene through programs like Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
- Managing primary health centers and ensuring the availability of medical facilities.
- Agriculture and Rural Development
- Supporting agricultural development through training, resources, and technology.
- Implementing schemes for irrigation, watershed management, and soil conservation.
- Promoting self-help groups (SHGs) and cooperatives for rural entrepreneurship.
- Infrastructure Development
- Developing rural infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public transportation.
- Ensuring access to clean drinking water and sanitation facilities.
- Promoting electrification and connectivity in rural areas.
- Social Welfare
- Implementing social welfare schemes for marginalized communities, including Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and women.
- Promoting programs for child welfare, elderly care, and disability support.
- Employment Generation
- Promoting skill development and vocational training programs to enhance employability.
- Implementing employment generation schemes like MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act).
- Environmental Conservation
- Promoting sustainable practices in agriculture and resource management.
- Implementing programs for afforestation, waste management, and biodiversity conservation.
- Coordination and Monitoring
- Coordinating with various government departments, NGOs, and community-based organizations for effective implementation of programs.
- Monitoring the progress of development projects and ensuring accountability.
- Community Participation
- Encouraging local communities to participate in decision-making processes and development initiatives.
- Facilitating the formation of village-level committees and organizations for better governance.
- Financial Management
- Managing the financial resources allocated for various development programs and ensuring transparency in expenditure.
- Mobilizing funds from state and central government schemes, as well as from other sources.
These functions collectively aim to promote holistic development in rural areas, ensuring that the needs and aspirations of the local population are addressed effectively.


